The second coursework is all about using sensors to interpret the state of the world around the sensing device.
In your coursework you will build a system which uses at least two sensors. You may wish to prototype elements of your sensing using the web sensor platform.
As an example of a sensing algorithm, here is a repetitive activity being sensed - click start below, and if you are quiet, you should be able to clap, and the number of claps being printed out should go up.
To understand how this code works, work through the exercises in this website, which will help you learn the basics of how sensor processing systems are developed.
Coursework doings
For the coursework, you will submit a proposal for a sensing system to build.
You will then prototype only the sensor processing aspect of this, i.e. the part which interprets the sensor data. You will not prototype the user interface, the server backend, physical hardware or anything else. These aspects of the system may be described in the design section of your report, but are not part of the practical work.
For the practical work, you will develop a sensing algorithm, a python script like the one above which takes in sensor data, processes that data, and outputs some kind of interpretation of the data. This will use the methods in the sections on sensor filtering and combination. We will expect your algorithm to run on the grovepi boards which are available in the lab unless you have already discussed something different with us.
Once the algorithm is built, you will use the methods in the section on testing of algorithms to quantify how well your system works, and in what circumstances it fails and why. This is an important part of the final report which is highly weighted, so don’t leave this till the last minute.
As the previous paragraphs perhaps made obvious, the final outcome of this work is a written report. You must also submit all code for your sensor algorithm, which we will run during marking so we can understand how your system works. Please make sure all code you submit does run, as we cannot mark non-running code.
Stuff for you to use in the labs
During the coursework, you will want to prototype things - often this involves sticking stuff together with tape, strapping raspberry pis or sensors onto objects. We have a bunch of stuff around in the lab, including foam, gaffa tape, cardboard, an empty cupboard if you want to prototype something inside a cupboard, a small trolley for prototyping moving projects etc. You can also take the raspberry pis out during the lab time, around the building, or even outside. You can also bring your own stuff to the lab sessions.
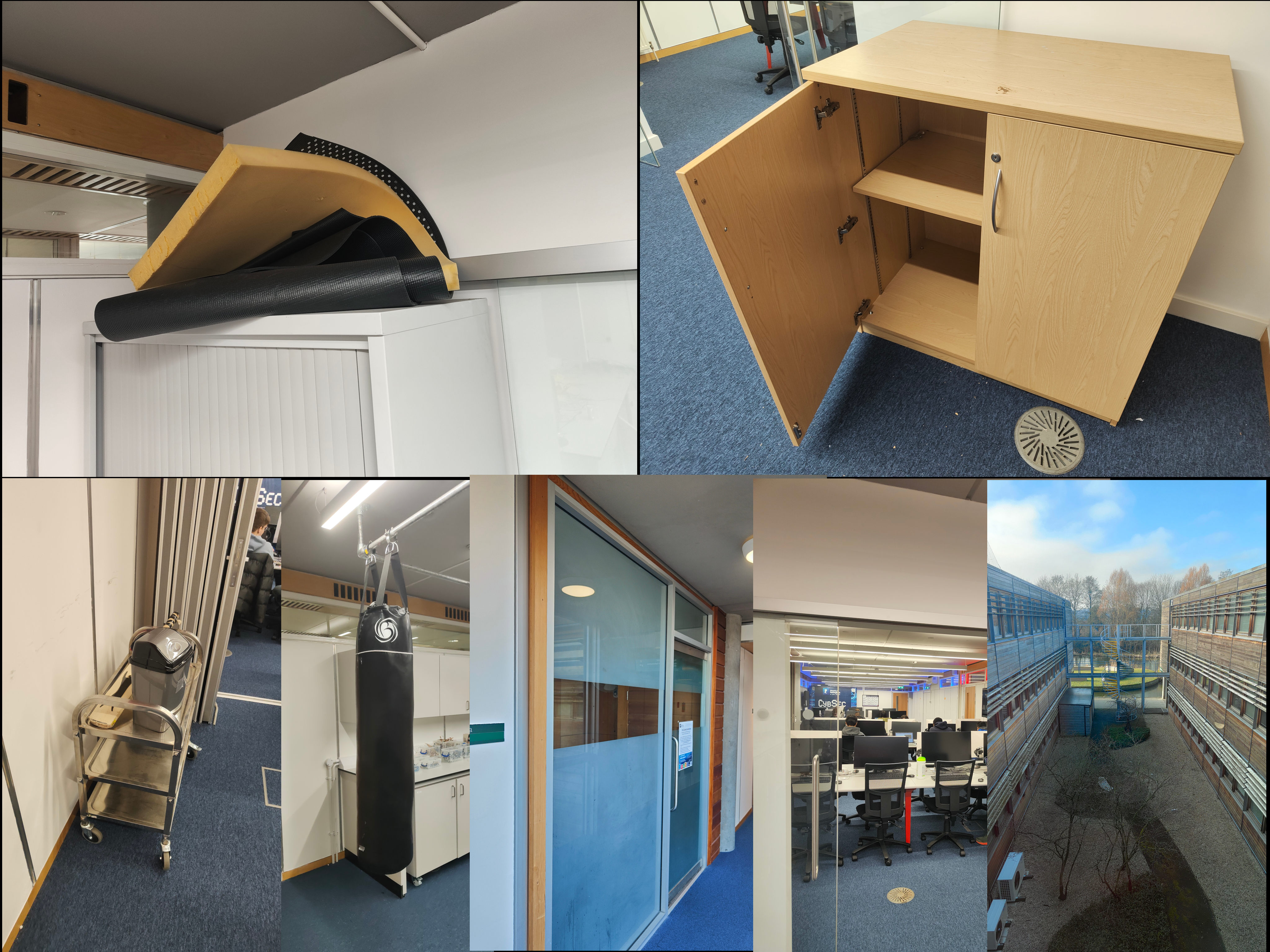

Here are some I made earlier…
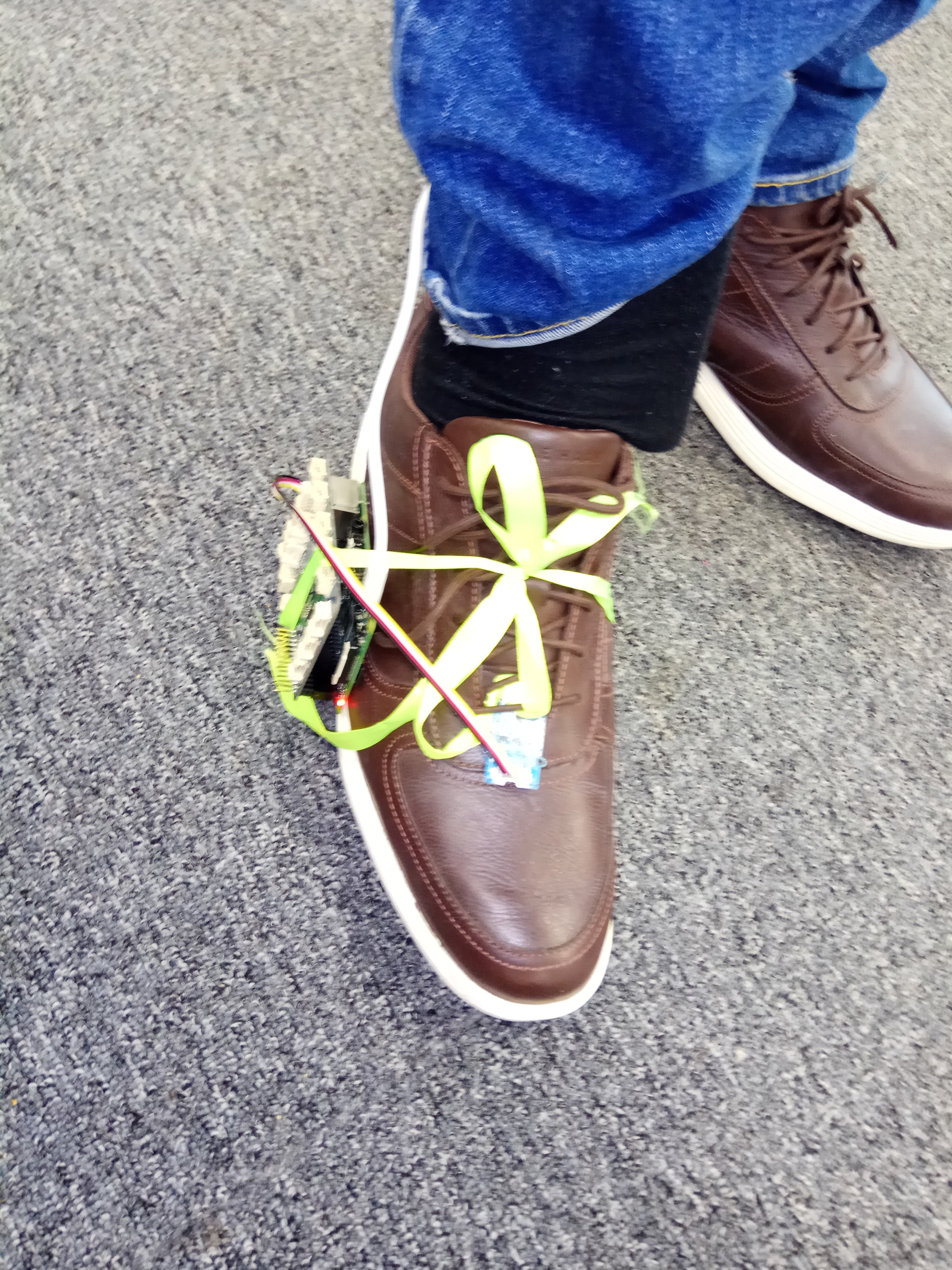
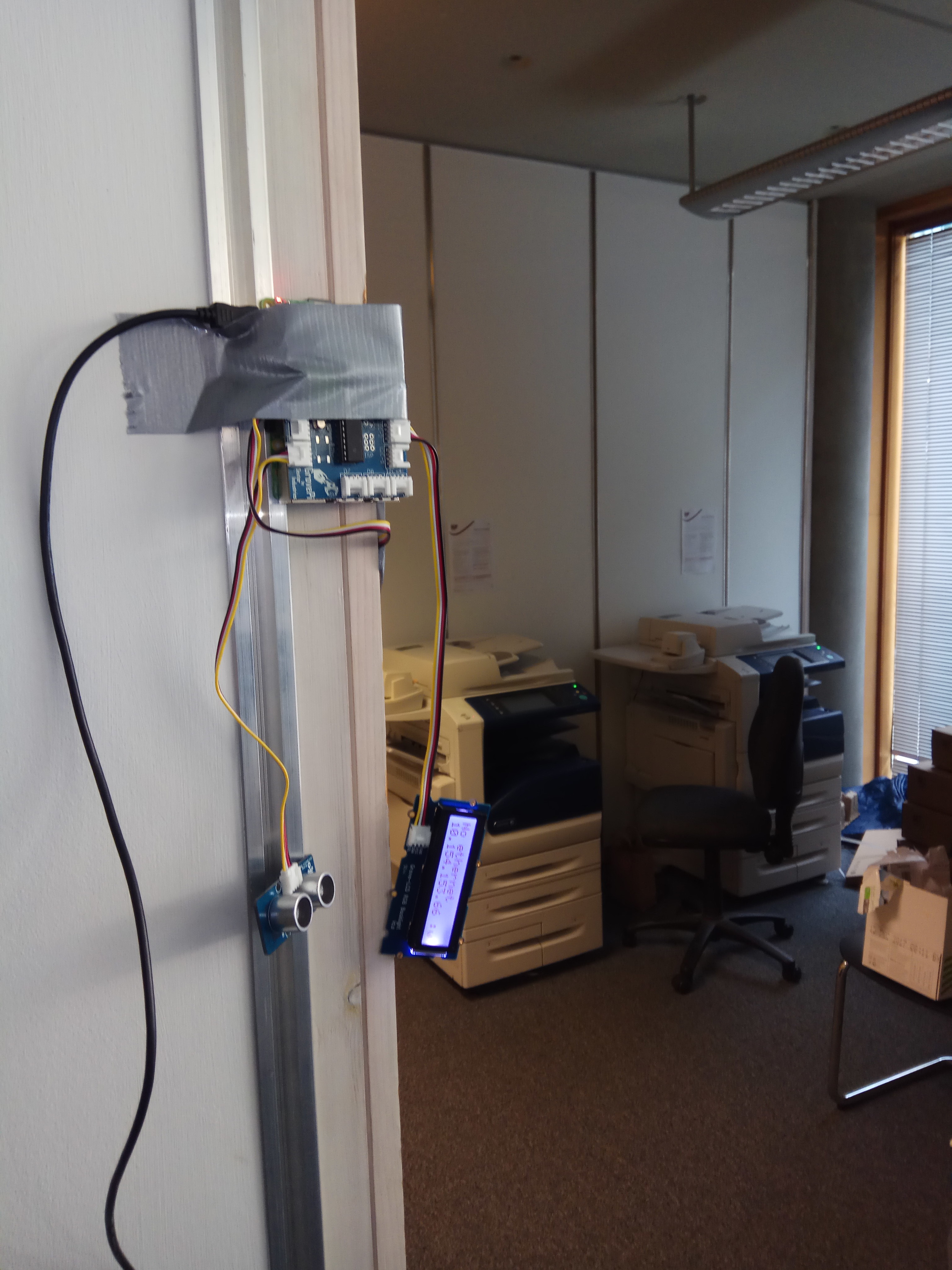
Some prototypes made by students on the course: